AI4TWINNING
Artificial Intelligence for the automated creation of multi-scale digital twins of the built world
Principal Investigators
Prof. Dr.-Ing. André Borrmann,
Chair of Computational Modeling and Simulation, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Daniel Cremers,
Chair of Computer Vision and Artificial Intelligence, Departments of Informatics and Mathematics
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Thomas H. Kolbe,
Chair of Geoinformatics, Department of Aerospace and Geodesy
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Frank Petzold,
Chair of Architectural Informatics, Department of Architecture
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Ludwig Hoegner,
Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Department of Aerospace and Geodesy
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Xiaoxiang Zhu,
Data Science in Earth Observation, Department of Aerospace and Geodesy
Motivation and Goals
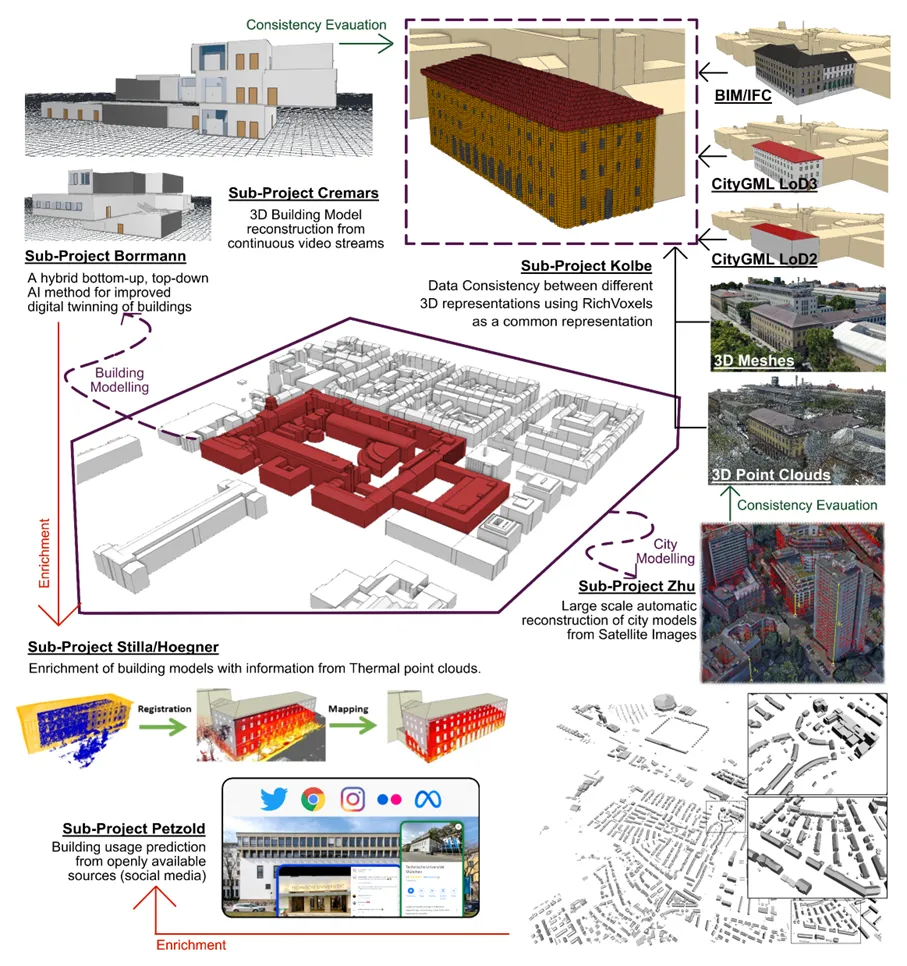
Digital modelling of the built word requires information abstractions at various scales and according to a range of competences. This project involves the unique generation of a system of interrelated digital twins of the built environment, spanning multiple resolution scales providing rich semantics and coherent geometry. We are researching a multi-scale, multi-method approach combining terrestrial, airborne, and spaceborne acquisition, with multiple sensor types (visible, thermal, LiDAR, Radar).
Recent Results
- Automatic pipeline for large-scale building model reconstruction from TomoSAR point clouds.
- Novel top-down-bottom-up method for point clouds processing incorporating construction knowledge.
Creation of indoor digital twin models for TUM Building 1 at the City Campus. - Generation of annotated datasets leveraging the learned features of facade elements.
- Registration of TIR point cloud with building model and projection of thermal intensities to façade.
- Automatic pipeline for voxelization of IFC, CityGML and Mesh Models to compare geometry and semantics using RichVoxels as a common representation.
Selected documentation
| Submitted journal paper | V Kostic, Q Khan, D Cremers, C Gehlen, J Timothy and T Kränkel, 2024: Efficient labelling of air-voids and aggregates in concrete and mortar using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy combined with Meta AI's Segment Anything Model. (Submission to Advanced Engineering Informatics planned in late 2024: Special Issue AI for the Built World) |
| Conference papers | L Schnürer, A Machner, 2023: Effects of the Chemical Composition of Synthetic Slags Compared to an Average Blast Furnace Slag. In: Proceedings in Civil Engineering, Volume 6, Issue 6. https://doi.org/10.1002/cepa.2933. Q Khan, M Hassan, V Kostic, V Golkov, C Gehlen and D Cremers, 2024: Improving the Detection of Air-Voids and Aggregates in Images of Concrete Using Generative AI. In GNI Symposium on AI for the Built World, 2024 V Kostic, Q Khan, D Cremers, C Gehlen, J Timothy and T Kränkel, 2024: Efficient labelling of air-voids and aggregates in concrete and mortar using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy combined with Meta AI's Segment Anything Model. In GNI Symposium on AI for the Built World, 2024 |
AI4TWINNING consists of 6 subprojects
- AI and Earth Observation for a Multi-scale 3D Reconstruction of the Built Environment
- Thermal 3D mapping and CNN analysis
- AI-based / knowledge-driven reconstruction of semantic building data using multiple image data sources
- Digital twin data consistency across multiple representations
- Knowledge-driven 3D Reconstruction from Camera Streams
- A hybrid top-down bottom-up AI method for improved digital twinning of buildings